"We can wait and observe how the economy develops." Federal Reserve Chairman Powell made a cautious statement at the press conference, and this sentence quickly became a key footnote for interpreting the market trend after this rate cut.
In the early morning of December 11, East 8th District time, the Federal Reserve announced that it would lower the federal funds rate target range by 25 basis points to 3.50% to 3.75%. This is the third consecutive 25 basis point rate cut by the Federal Reserve since September this year. After consecutive rate cuts, internal divisions within the Federal Reserve and Powell's cautious stance on future policy have instead triggered more complex turbulence in the financial markets.

I. Decision Implemented: Expected Rate Cut and Internal Divergence
Although the Federal Reserve's rate cut decision was anticipated by the market, the decision-making process and the signals released after the meeting were full of complexity. The following table summarizes the key information from this meeting:
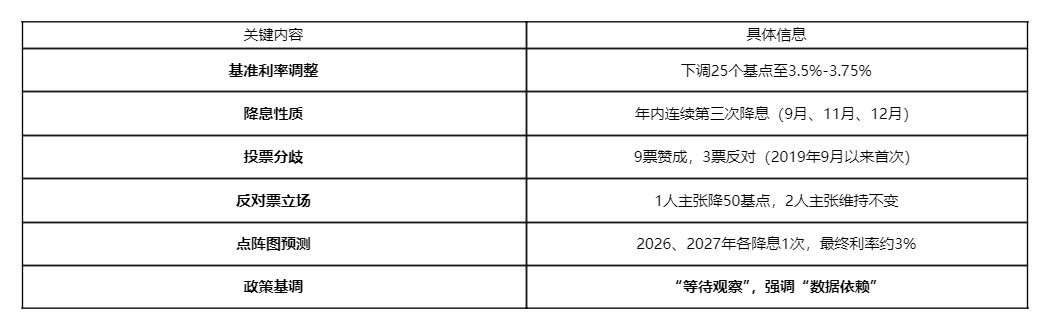
The statement from this meeting reintroduced language that future policy adjustments regarding "degree and timing" will depend on subsequent data. The market interpreted this as a clear signal from the Federal Reserve: any further easing policies in the future will set a higher threshold.
II. Divergence and Volatility After the Rate Cut
After the decision was announced, global financial markets showed a "pulse-like" reaction, with rapid divergence in the trends of different asset classes.
● In traditional assets, US stocks responded positively, with the Dow Jones Index closing up about 1%, and the regional bank index, which is sensitive to interest rates, surged by 3.3%. At the same time, bond prices rose, and the yield on the 10-year US Treasury fell accordingly.
● The foreign exchange and commodity markets showed a different picture: the US Dollar Index fell by about 0.6%, hitting a new low in over a month; precious metals strengthened, with silver reaching a new high; and the crude oil market staged a V-shaped reversal.
● The most watched cryptocurrency market experienced a typical "sell the news" scenario. Taking bitcoin as an example, its price surged after the decision was announced, but quickly fell back by more than 2.2%. Other major cryptocurrencies such as ethereum also showed similar spike-and-retrace trends.
III. Why Did the Rate Cut Trigger Market Turbulence?
The root cause of such divergent market trends is not the rate cut itself, but the deeper signals conveyed by this meeting.
● First, the market follows the rule of "buy the rumor, sell the news". This 25 basis point rate cut had already been fully priced in and digested by the market. When expectations were realized, some investors chose to take profits, leading to a pullback in asset prices.
● Second, the policy path has shifted to "cautious" and "limited". Goldman Sachs analysts clearly pointed out that the Federal Reserve's "phase of precautionary rate cuts has ended." Whether rate cuts will continue in the future will depend entirely on whether labor market data further deteriorates. Powell also emphasized that the current interest rate is already "at the higher end of the neutral range," and the Federal Reserve can "wait and observe."
● Furthermore, the Federal Reserve faces a dilemma. On one hand, the job market has shown signs of cooling, which is the core driver of this rate cut. Internal estimates by the Federal Reserve indicate that recent non-farm employment data may have been overestimated, and the actual monthly increase in employment may be at a relatively low level of only 80,000-90,000 people.
● On the other hand, inflationary pressures still exist. The Federal Reserve's preferred inflation indicator (PCE) remains far above the 2% target. Powell partly blamed the Trump administration's tariff policies for inflation, believing they caused a "one-time price shock." This combination of "declining employment" and "sticky inflation" makes the Federal Reserve's decision-making exceptionally difficult.
IV. The Market Will Closely Watch Employment Data and Political Variables
Looking ahead, the direction of the financial markets will mainly depend on the evolution of two core variables.
● Core Variable One: The "Thermometer" of the Labor Market. As analyzed by Goldman Sachs, the rationality of future easing policies will depend on whether labor market data can reach a "higher threshold". Market institutions generally believe that if, before spring 2026, non-farm employment continues to fall below 100,000 and the unemployment rate exceeds 4.5%, it may trigger the Federal Reserve to restart rate cuts. Otherwise, the Federal Reserve may only implement 1-2 more rate cuts throughout the year.
● Core Variable Two: The Political Challenge to Policy Independence. Political pressure from the White House has intensified market concerns about the continuity of future policies. US President Trump criticized the rate cut as too small after the decision and revealed that he had already decided on Powell's successor. Analysts point out that the future choice of Federal Reserve Chairman and their policy tendencies will become a major variable affecting market expectations.
V. Cryptocurrency: The Interplay of Independent Logic and Macroeconomic Impact
For the cryptocurrency market, the Federal Reserve's policy impact mechanism is more complex. It is not simply "rate cuts are good for risk assets".
● The liquidity mechanism is more important than the interest rate level. Professional analysis points out that the market should pay more attention to whether the Federal Reserve has injected liquidity into the financial system through operations (such as Treasury purchases), which directly affects the willingness and ability of market makers to quote for risk assets such as cryptocurrencies. If there is only a rate cut without substantial liquidity improvement, the market may react indifferently.
● "Expectation management" determines price trends. There have been many instances in cryptocurrency history where prices fell after rate cuts, because the market had already priced in the positive news and traders took profits. This is consistent with the current "spike and retrace" behavior of bitcoin.
● Different coins have vastly different sensitivities. Because altcoins generally have shallower trading depth and higher leverage, they are more sensitive to changes in funding costs than bitcoin. When liquidity tightens or market volatility increases, altcoins often experience larger percentage declines.
● In addition, the potential rate hike move by the Bank of Japan, as another important macro variable, may exert short-term pressure on the crypto market by draining global liquidity. Some analysts believe that the cryptocurrency market may enter a consolidation phase lasting until mid-2026, preparing for the next cycle.
Global markets are digesting a key shift: the Federal Reserve's policy focus has shifted from "preventing economic downturn" to "struggling to balance inflation and employment". The return of the "degree and timing" language in the meeting statement sets a higher data threshold for future rate cuts.
Powell pointed the finger at tariffs for inflation, while Trump expressed dissatisfaction with the size of the rate cut. This subtle game between the central bank and the White House adds more uncertainty to the monetary policy outlook for 2026. For frontier risk assets such as cryptocurrencies, the era of unlimited liquidity easing expectations has ended, and the market will have to find direction again in a more complex macro environment that relies more on specific economic data.



