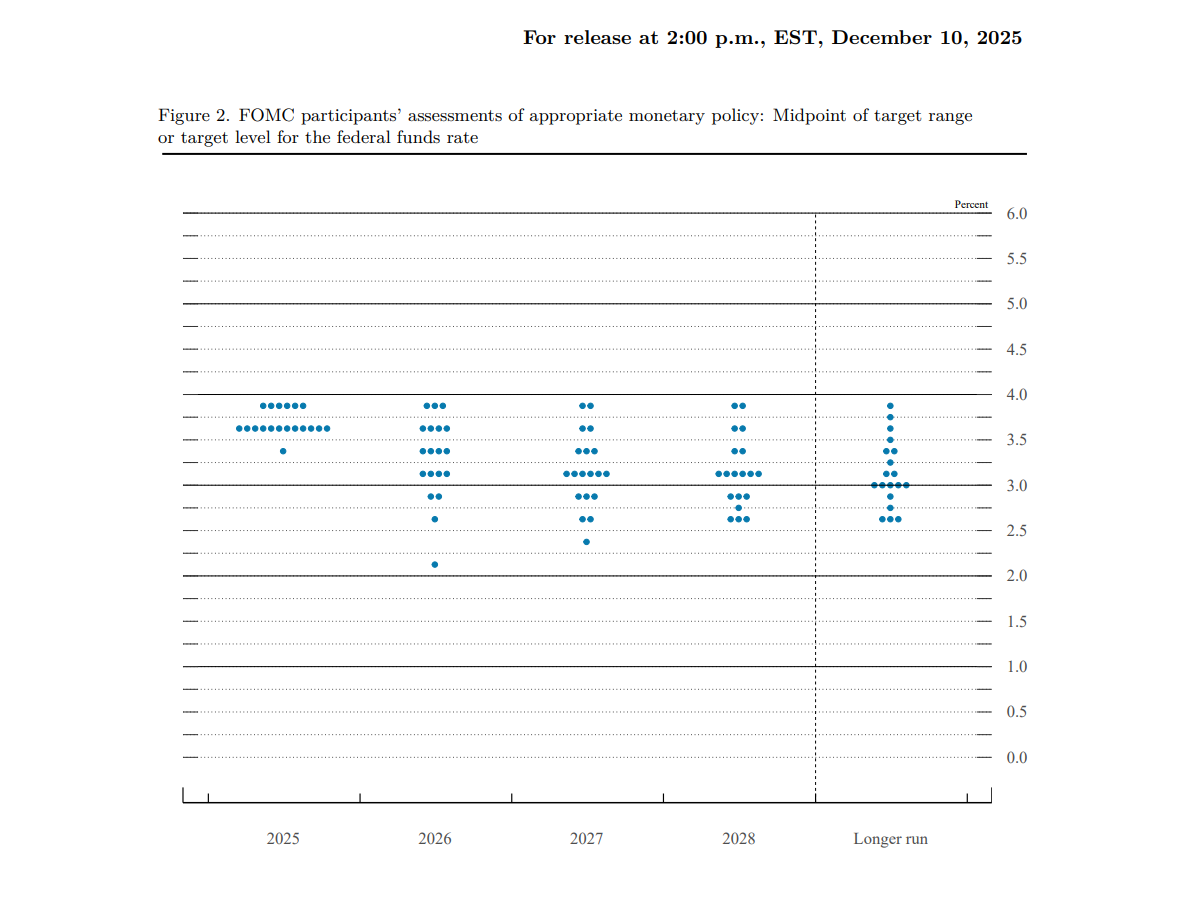
Federal Reserve's Major Shift: From QT to RMP, How Will the Market Transform by 2026?
The essence of RMP, the mystery surrounding its scale, and its impact on risk assets.
Author: Wang Yongli
In the ever-changing global financial markets, every decision made by the Federal Reserve tugs at the nerves of countless investors. In recent years, our economic life has felt like riding a roller coaster, sometimes accelerating, sometimes slowing down. Among the many policy tools, a new strategy called "Reserve Management Purchases" (RMP) is quietly emerging, signaling that the financial markets may be ushering in a new chapter of "stealth easing."
The Key Turning Point of 2025: The End of QT and the Debut of RMP
Imagine the fourth quarter of 2025, when the global financial markets reach an important milestone. The Federal Reserve, the world's most influential central bank, makes a historic decision. After nearly three years of "Quantitative Tightening" (QT)—that is, large-scale balance sheet reduction—they officially announce: On December 1, 2025, the QT program will end!
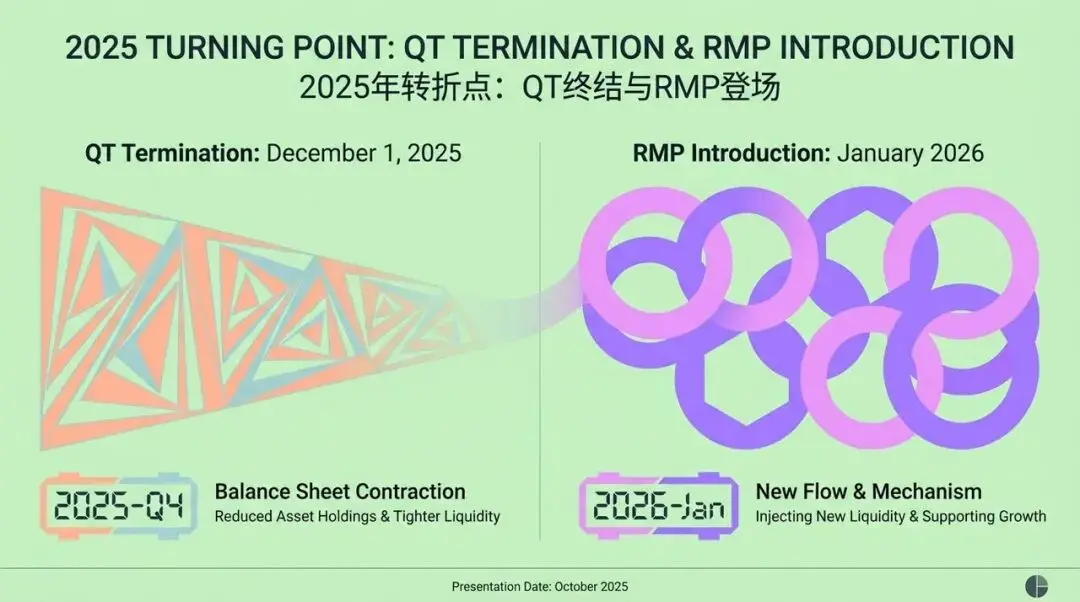
However, the story does not end there. Immediately after, in January 2026, a brand-new strategy, RMP (Reserve Management Purchases), officially debuts. This somewhat academic-sounding new tool caused a huge stir on Wall Street as soon as it was announced. The Federal Reserve officially defines it as a "technical operation" aimed at maintaining an "ample" level of liquidity in the financial system to meet naturally growing demand.
The Federal Reserve's official language tends to portray it as a routine, technical adjustment to ensure the smooth operation of the financial system. But this stands in stark contrast to the market's widespread interpretation—"stealth easing."
However, the market generally interprets it as a form of "stealth easing," believing that the Federal Reserve may be about to "flood the market" with liquidity again. So, which of these two diametrically opposed interpretations is closer to the truth? How will the arrival of RMP affect our future investment strategies?
The End of QT: The Financial "Vacuum Cleaner" Meets Resistance
To understand the far-reaching impact of RMP, we must first look back at the end of QT. Before the end of 2025, the Federal Reserve's quantitative tightening policy was like a giant "vacuum cleaner," continuously sucking liquidity out of the global financial system. Since its launch in June 2022, in just three years, the Fed's balance sheet shrank from a peak of nearly $9 trillion to about $6.6 trillion, meaning $2.4 trillion in liquidity vanished from the market.
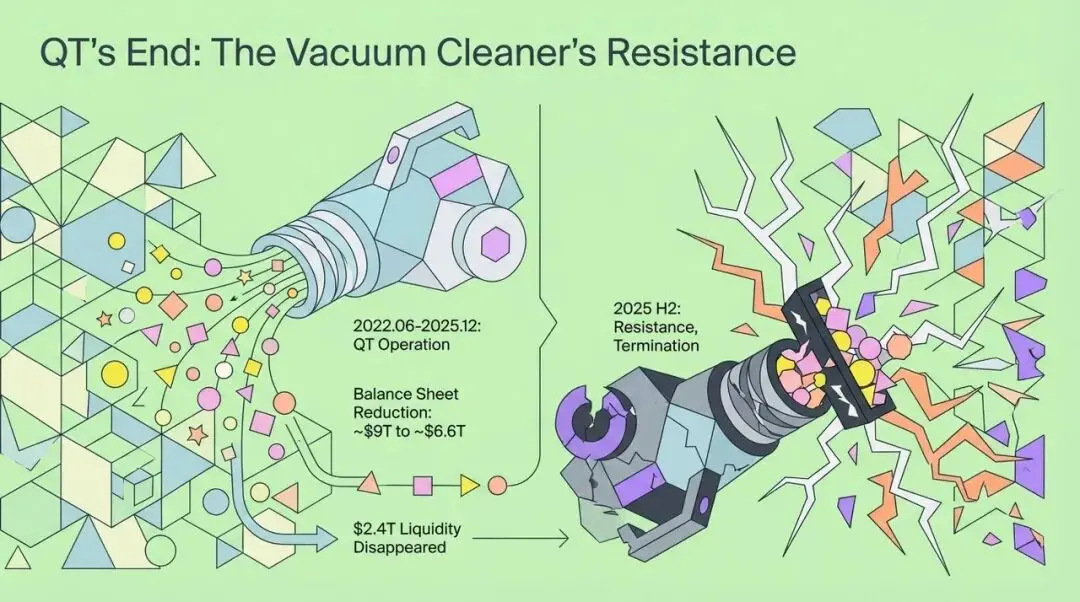
However, by the second half of 2025, this "vacuum cleaner" encountered unprecedented resistance. The Federal Reserve decided at its October meeting that year to end QT, not because it had fully achieved its inflation target, but out of deep concern for financial stability.
We can liken the money market at that time to a giant reservoir. Although the total amount of water seemed ample, most of the water was trapped in a few "tanks," while the vast "fields"—the microeconomic sectors that truly needed funds—remained dry or even cracked. This structural imbalance in liquidity distribution was the fundamental reason for the Fed's shift to RMP.
Micro Liquidity Crisis Signals: The Divergence Between SOFR and IORB
What forced the Federal Reserve to abandon balance sheet reduction? A series of "micro liquidity crisis" signals that emerged in 2025 were key. The most notable was the strange divergence—a significant positive spread—between the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR) and the Interest on Reserve Balances (IORB).
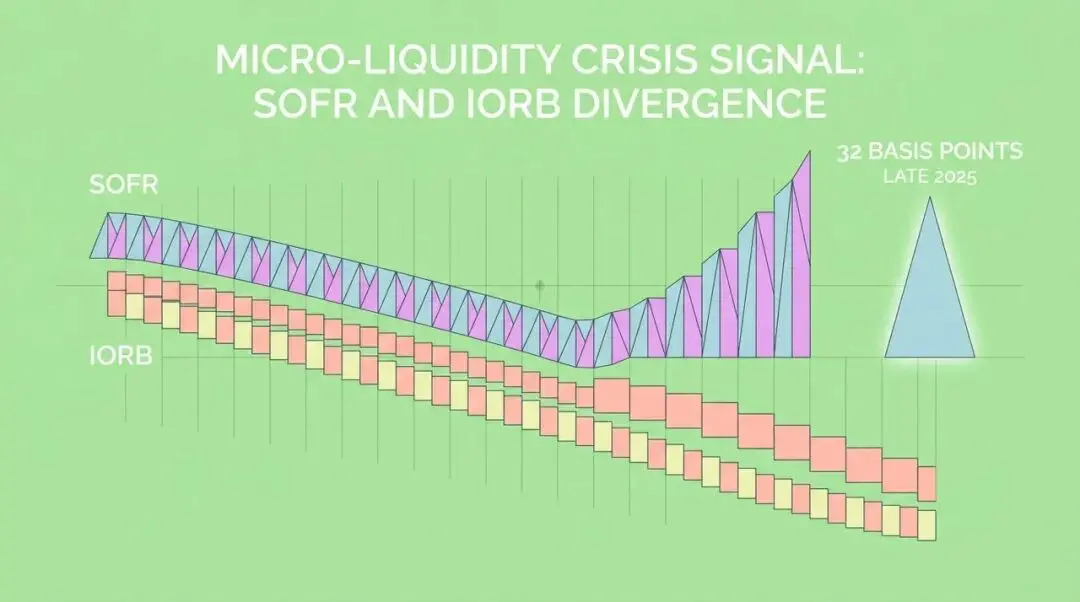
This meant that banks would rather pay a higher premium to borrow money in the market (SOFR) than use their seemingly "ample" reserves at the Federal Reserve (IORB). This phenomenon revealed deep contradictions within the financial system:
- Extremely uneven liquidity distribution: Although total bank reserves appeared sufficient, they were actually concentrated in a few large institutions.
- Changes in bank behavior: Under regulatory pressure, banks' demand for liquidity became more cautious than ever, and even with idle funds, they were reluctant to lend easily.
Another core factor was the imbalance between the supply and demand for collateral and cash. To finance the huge fiscal deficit, the U.S. Treasury issued a record number of Treasury bonds. These newly issued bonds flooded the repo market like a tsunami, requiring a large amount of cash to absorb them. However, the QT policy had already drained cash from the system, resulting in "too much collateral chasing too little cash," directly pushing up repo rates.
The RMP Mechanism: "Technical Fix" or "Stealth Easing"?
Now, let's take a closer look at the RMP mechanism. The Federal Reserve defines it as a technical operation aimed at keeping bank reserves at an "ample" level. This is fundamentally different from Quantitative Easing (QE).
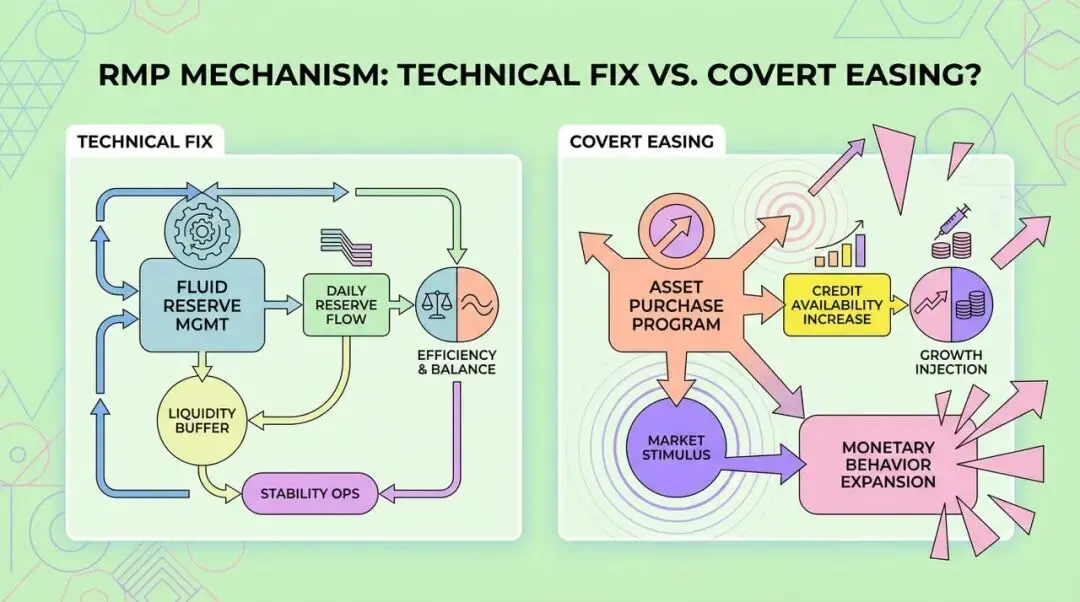
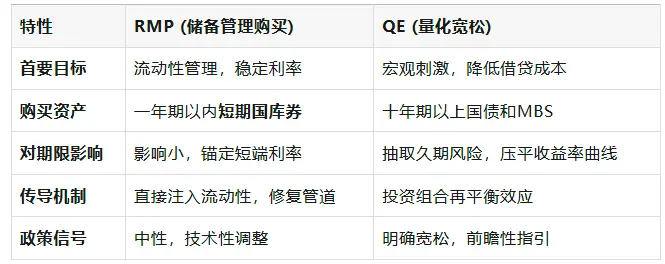
There are three reasons why RMP chooses to purchase short-term Treasury bills:
- Similar risk characteristics: Short-term Treasury bills and bank reserves are both highly liquid and considered "quasi-cash," so buying them involves almost no duration risk transfer.
- Avoiding additional stimulus: This helps the Fed maintain a "neutral" policy stance and avoid being interpreted by the market as aggressively easing monetary policy.
- Coordinating with Treasury's debt issuance strategy: In the face of massive short-term Treasury issuance, RMP purchases actually provide liquidity support for the Treasury's short-term financing.
The Mystery of RMP Scale: Wall Street's Divergence and Market Variables
In December 2025, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) will officially announce the details of RMP and plans to implement it in January 2026. However, there are huge differences among Wall Street analysts regarding the specific scale of RMP purchases, which also constitutes the biggest market variable in the first quarter of 2026.
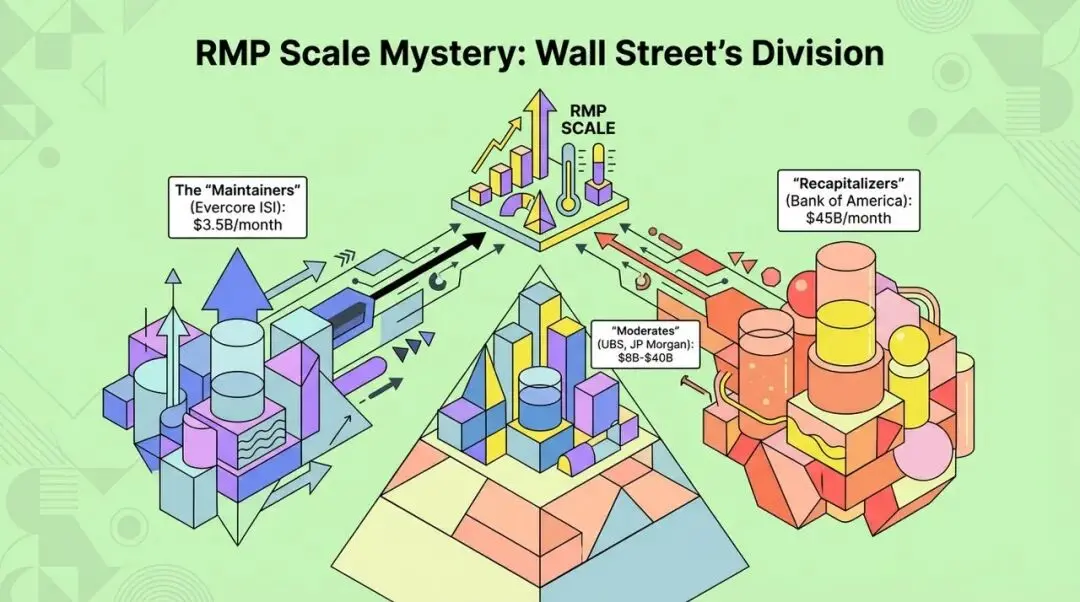
The market is mainly divided into two camps:
- "Maintenance camp": They believe that the current reserve level is already relatively balanced, and the purpose of RMP is only to offset the natural growth of currency in circulation. For example, Evercore ISI predicts a monthly purchase scale of about $3.5 billion.
- "Replenishment camp": Represented by Bank of America strategist Mark Cabana, they believe the Fed "overdid it" during QT, causing reserves to fall below the "minimum comfortable level," so a large-scale replenishment is needed. They predict monthly purchases as high as $45 billion (normal demand $20 billion + additional replenishment $25 billion).
These two very different forecasts will lead to huge differences in market expectations for future liquidity.
How Will RMP Affect Risk Assets? "Crowding-Out Effect" and "Balance Sheet Release"
Although the Federal Reserve emphasizes that RMP mainly purchases short-term Treasury bills and theoretically should not have QE-like effects on asset prices, the reality of market operations is more complex.
1. Crowding-Out Effect
When the Fed intervenes massively in the short-term Treasury market, it will suppress yields on short-term Treasuries. To maintain returns, money market funds may allocate capital to higher-yielding commercial paper, repo lending, or even short-term corporate bonds.
This "crowding-out effect" will prompt liquidity to flow from the government sector to the private credit sector, thereby indirectly boosting the performance of risk assets.
2. Primary Dealers' Balance Sheet Release
RMP directly reduces the pressure on primary dealers to hold Treasury inventory. When their balance sheet space is freed up, they have more capacity to provide liquidity intermediation for other markets, such as margin financing in the stock market or market making in corporate bonds. The restoration of this intermediation capacity is a key support for the performance of risk assets.

Regulation and Fiscal Policy: The Dual Pressure Behind RMP
Federal Reserve Governor Steven Miran proposed a "regulation-driven" hypothesis. He believes that the post-financial crisis regulatory framework, such as the Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR) and Basel III, forces banks to hold high-quality liquid assets far in excess of actual operational needs. In regulatory calculations and real stress tests, cash (reserves) is often preferred over Treasuries, leading to a rigid and elevated "minimum comfortable reserve level." RMP is essentially a central bank balance sheet expansion to meet liquidity needs created by regulation.
In addition, the implementation of RMP cannot be separated from an important background—the continued high level of the U.S. federal deficit.
"The Treasury issues short-term Treasury bills, and the Fed purchases short-term Treasury bills through RMP"—this closed-loop operation is essentially very close to "debt monetization." The Fed becomes the marginal buyer of the Treasury's short-term debt, which not only lowers the government's short-term financing costs but also raises concerns about the weakening of central bank independence and the unanchoring of inflation expectations. This "fiscal dominance" pattern will further dilute the purchasing power of fiat currency, thus benefiting physical assets such as gold.
Asset Forecasts: Market Reactions Under Aggressive Scenarios
If RMP purchases reach an aggressive scenario of $45 billion per month, how will the market react?
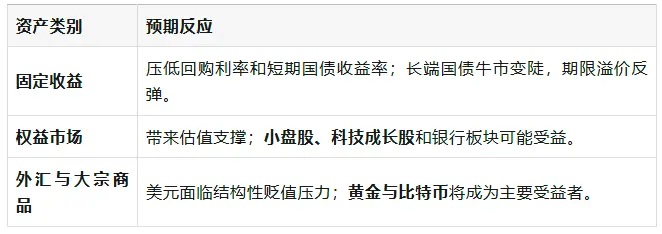

RMP Scenario Analysis and Institutional Investor Strategy Recommendations
Given the uncertainty of RMP scale, we can make the following scenario assumptions:
- Scenario A: Soft Landing and Technical Fix (Probability 40%)
- The Fed purchases $20-30 billion per month.
- Result: The stock market rises moderately, volatility declines, the dollar moves sideways, and the yield curve normalizes.
- Scenario B: Liquidity Tsunami and Reflation (Probability 35%)
- The Fed purchases more than $45 billion per month.
- Result: Risk assets experience a "melt-up," commodities soar, inflation expectations become unanchored, and the Fed may be forced to turn hawkish later.
- Scenario C: Policy Mistake and Liquidity Shock (Probability 25%)
- The Fed purchases only $3.5 billion.
- Result: The repo market experiences another crisis, basis trades blow up, the stock market undergoes a sharp correction, and the Fed may need to intervene urgently.
For institutional investors, 2026 will require corresponding strategic adjustments:
- Focus on structural changes in volatility: As QT ends, volatility driven by liquidity tightening will decline, so consider shorting the VIX index.
- Allocate a "fiscal dominance" hedging portfolio: Overweight gold and physical assets to hedge against the risk of declining fiat currency purchasing power.
- Equity strategy: Tactically overweight small-cap and technology stocks, and closely monitor inflation data.
- Fixed income: Avoid simply holding cash or short-term Treasuries, and use yield curve steepening trades to earn excess returns.
Conclusion: Liquidity Dominance in the New Paradigm
The transition from "Quantitative Tightening" to "Reserve Management Purchases" marks the substantive end of the Federal Reserve's attempt at monetary policy normalization. This reveals a deeper reality: the modern financial system's dependence on central bank liquidity has become a structural chronic issue. RMP is not just a technical "pipeline repair," but a compromise in the face of dual pressures from "regulation dominance" and "fiscal dominance."
For investors, the main theme of 2026 will no longer be "How much will the Fed raise rates?" but "How much money does the Fed need to print to keep the system running?" In this new paradigm, liquidity will once again become the decisive force in asset prices. Understanding RMP and mastering its potential impact will help us better understand and respond to future market changes.
Original link
Disclaimer: The content of this article solely reflects the author's opinion and does not represent the platform in any capacity. This article is not intended to serve as a reference for making investment decisions.
You may also like
"Validator's Pendle" Pye raises $5 million, enabling SOL staking yields to be tokenized
There are truly no creative bottlenecks in the financialization of Web3.

DiDi has become a digital banking giant in Latin America
DiDi has successfully transformed into a digital banking giant in Latin America by addressing the lack of local financial infrastructure, building an independent payment and credit system, and achieving a leap from a ride-hailing platform to a financial powerhouse. Summary generated by Mars AI. This summary was produced by the Mars AI model, and its accuracy and completeness are still being iteratively improved.

Fed rate cuts in conflict, but Bitcoin's "fragile zone" keeps BTC below $100,000
The Federal Reserve cut interest rates by 25 basis points, but the market interpreted the move as hawkish. Bitcoin is constrained by a structurally fragile range, making it difficult for the price to break through $100,000. Summary generated by Mars AI This summary was generated by the Mars AI model, and the accuracy and completeness of its content are still being iteratively updated.

Full text of the Federal Reserve decision: 25 basis point rate cut, purchase of $4 billion in Treasury bills within 30 days
The Federal Reserve cut interest rates by 25 basis points with a 9-3 vote. Two members supported keeping rates unchanged, while one supported a 50 basis point cut. In addition, the Federal Reserve has restarted bond purchases and will buy $40 billion in Treasury bills within 30 days to maintain adequate reserve supply.